Latest revision as of 04:07, 8 January 2016
Information about message (contribute ) This message has no documentation.
If you know where or how this message is used, you can help other translators by adding documentation to this message.
Message definition (Orientation Selective Ganglion Cell )
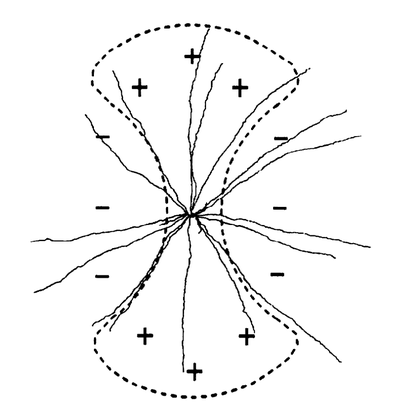
[[Image: arbors1.png|thumb|400px|The receptive field of an orientation selective ganglion cell, with an excitatory center (+) and inhibitory surround (-).<ref name="Bloomfield">Bloomfield SA(1994) Orientation-sensitive amacrine and ganglion cells in the rabbit retina. J Neurophysiol 71:1672-1691.
[[Image: arbors1.png|thumb|400px|The receptive field of an orientation selective ganglion cell, with an excitatory center (+) and inhibitory surround (-).<ref name="Bloomfield">Bloomfield SA(1994) Orientation-sensitive amacrine and ganglion cells in the rabbit retina. J Neurophysiol 71:1672-1691.
http://jn.physiology.org/content/71/5/1672.abstract?ijkey=4cfa4066fd39257147ad90ee1df8864247a4132f&keytype2=tf_ipsecsha</ref>]]
===AMPA and NMDA Receptors===
AMPA and NMDA receptors have been found to play a significant role in signal integration in ganglion cells found in rabbit retinas.<ref name="Marc2">Marc RE (1999) Mapping glutamatergic drive in the vertebrate retina with a channel-permeant organic cation. J Comp Neurol, 407(1):47-64. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19990428)407:1%3C47::AID-CNE4%3E3.0.CO;2-0/abstract</ref> AGB cation was used to evaluate the differences in permeability of the different ganglion cells types when kainate, AMPA, and NMDA receptors were activated. Translation [[Image: arbors1.png|thumb|400px|The receptive field of an orientation selective ganglion cell, with an excitatory center (+) and inhibitory surround (-).<ref name=\"Bloomfield\">Bloomfield SA(1994) Orientation-sensitive amacrine and ganglion cells in the rabbit retina. J Neurophysiol 71:1672-1691. The receptive field of an orientation selective ganglion cell, with an excitatory center (+) and inhibitory surround (-).
[1] AMPA와 NMDA 수용체(AMPA and NMDA Receptors)
AMPA와 NMDA 수용체는 토끼 망막에서 발견된 신경절 세포의 신호통합에 있어 중요한 역할을 하는 것으로 발혀졌습니다.
[2] Kainate, AMPA 및 NMDA 수용체가 활성화 되었을 때 서로 다른 신경절 세포 종류들의 투과성을 평가하기 위하여 AGB 양이온이 사용되었습니다.
↑ Bloomfield SA(1994) Orientation-sensitive amacrine and ganglion cells in the rabbit retina. J Neurophysiol 71:1672-1691.
http://jn.physiology.org/content/71/5/1672.abstract?ijkey=4cfa4066fd39257147ad90ee1df8864247a4132f&keytype2=tf_ipsecsha
↑ Marc RE (1999) Mapping glutamatergic drive in the vertebrate retina with a channel-permeant organic cation. J Comp Neurol, 407(1):47-64. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19990428)407:1%3C47::AID-CNE4%3E3.0.CO;2-0/abstract