Latest revision as of 03:49, 8 January 2016
Information about message (contribute ) This message has no documentation.
If you know where or how this message is used, you can help other translators by adding documentation to this message.
Message definition (On-Off Direction-Selective Ganglion Cell )
Direction selective (DS) cells in the retina are neurons that respond differentially to the direction of a visual stimulus. The term is used to describe a group of neurons that preferentially "gives a vigorous discharge of impulses when a stimulus is moved through its receptive field in one direction." <ref name="barlow1965">H. B. Barlow and W. R. Levick (1965) [http://jp.physoc.org/content/178/3/477.full.pdf The Mechanism of Directionally Selective Units in Rabbit's Retina] J. Physiol. <strong>178</strong>: 477-504</ref> There are three known types of DS cells in the vertebrate retina of the mouse, ON/OFF DS [[Ganglion Cell|Ganglion Cells]], ON DS Ganglion Cells (which respond to the leading edge of a bright stimulus) and OFF DS Ganglion Cells (which respond only to the trailing edge of a bright stimulus). Each has a distinctive physiology and anatomy.<ref name="wiki">"Motion Sensing in Vision." Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_Sensing_in_Vision (Accessed April 02, 2012).</ref> The rest of this page will only apply to ON/OFF DS Ganglion Cells.
Direction selective (DS) cells in the retina are neurons that respond differentially to the direction of a visual stimulus. The term is used to describe a group of neurons that preferentially "gives a vigorous discharge of impulses when a stimulus is moved through its receptive field in one direction." <ref name="barlow1965">H. B. Barlow and W. R. Levick (1965) [http://jp.physoc.org/content/178/3/477.full.pdf The Mechanism of Directionally Selective Units in Rabbit's Retina] J. Physiol. <strong>178</strong>: 477-504</ref> There are three known types of DS cells in the vertebrate retina of the mouse, ON/OFF DS [[Ganglion Cell|Ganglion Cells]], ON DS Ganglion Cells (which respond to the leading edge of a bright stimulus) and OFF DS Ganglion Cells (which respond only to the trailing edge of a bright stimulus). Each has a distinctive physiology and anatomy.<ref name="wiki">"Motion Sensing in Vision." Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_Sensing_in_Vision (Accessed April 02, 2012).</ref> The rest of this page will only apply to ON/OFF DS Ganglion Cells.
== Physiology ==
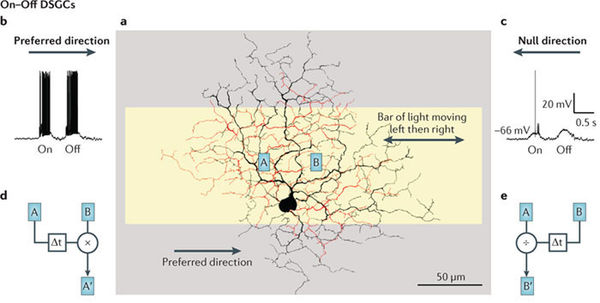
[[File:ONOFFDCSG1.jpg|thumb|right|600px|Diagram showing the response of ON/OFF DSGC to stimulus in the null and preferred direction. Inputs are multiplied in the preferred direction, and suppressed in the null direction.<ref name = "vaney2011">D. I. Vaney, B. Sivyer, and W. R. Taylor (2012). Direction selectivity in the retina: symmetry and asymmetry in structure and function. Nature Neuroscience <strong>13</strong> (3): 194-208</ref>]]
ON/OFF DSGCs act as local motion detectors. If a bright stimulus (e.g., a light) is moving in the direction of the cell's preference, the cell will fire at both the leading and trailing edge. An important contrast is that bright stimuli moving opposite the preferred direction (called the null direction), elicit little or no response <ref name="wiki" />. The response to stimulus is independent of many stimulus properties, including size, shape, color, and speed.
These cells have a center-surround structure, and the size of the [[Dendrite|dendrite]] correlates with the size of the center receptive field. <ref name="barlow1965" /> Translation 망막에 있는 방향 선택성 세포들은 시각적 자극의 방향에 다르게 반응하는 신경세포들입니다. 이 단어는 \"자극이 수용장에서 한 방향으로 움직일 때 특히 격렬하게 신호를 발생하는” 한 무리의 신경세포를 묘사하는 데 쓰입니다<ref name=\"barlow1965\">H. B. Barlow and W. R. Levick (1965) [http://jp.physoc.org/content/178/3/477.full.pdf The Mechanism of Directionally Selective Units in Rabbit's Retina] J. Physiol. <strong>178</strong>: 477-504</ref> 생쥐의 망막에선 세 종류의 방향 선택성 세포들이 알려져 있습니다; ON/OFF 방향 선택성 신경절 세포, ON 방향 선택성 신경절 세포(밝은 자극의 이끄는 선두 가장자리에 반응) 및 OFF 방향 선택성 신경절 세포(밝은 자극의 끌리는 꼬리 부분에만 반응)입니다. 각각의 세포는 독특한 생리 및 해부학적 구조를 갖고 있습니다.<ref name=\"wiki\">\"Motion Sensing in Vision.\" Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_Sensing_in_Vision (Accessed April 02, 2012).</ref> 이 페이지의 나머지 부분의 내용은 ON/OFF 방향 선택성 신경절 세포에만 해당되는 내용입니다. 망막에 있는 방향 선택성 세포들은 시각적 자극의 방향에 다르게 반응하는 신경세포들입니다. 이 단어는 \"자극이 수용장에서 한 방향으로 움직일 때 특히 격렬하게 신호를 발생하는” 한 무리의 신경세포를 묘사하는 데 쓰입니다[1] [2]
생리(Physiology) 반응이 없는 방향과 선호하는 방향에서 자극에 대해 ON/OFF 방향 선택성 신경절 세포가 반응하는 것을 보여주는 모식도. 입력신호는 선호하는 방향에서는 배가되고 반응이 없는 방향에서는 억제됩니다.
[3] ON/OFF방향 선택성 신경절 세포는 국소적인 움직임 탐지기의 역할을 합니다. 만일 밝은 자극(예를 들어 빛)이 세포가 선호하는 방향으로 움직이면 세포는 이끄는 선두 가장자리와 끌리는 꼬리 쪽 가장자리 모두 에서 신호를 발사합니다. 중요한 대비로써, 밝은 자극이 선호 방향의 반대 방향(반응이 없는 방향)으로 움직이는 경우 매우 적거나 반응이 아예 없게 됩니다.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag;
refs with no content must have a name 자극에 대한 반응은 크기, 모양, 색깔, 속도 등과 같은 자극의 여러 가지 성질들로부터 독립적입니다. 이들 세포들은 중심-주변 구조를 가지고 있으며 수상돌기의 크기는 중심 수용장의 크기와 관련이 있습니다.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag;
refs with no content must have a name
↑ H. B. Barlow and W. R. Levick (1965) The Mechanism of Directionally Selective Units in Rabbit's Retina J. Physiol. 178 : 477-504
↑ \"Motion Sensing in Vision.\" Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_Sensing_in_Vision (Accessed April 02, 2012).
↑ D. I. Vaney, B. Sivyer, and W. R. Taylor (2012). Direction selectivity in the retina: symmetry and asymmetry in structure and function. Nature Neuroscience 13 (3): 194-208