Difference between revisions of "J-RGC"
From Eyewire
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | JAM-B cells are a subcategory of retinal ganglion cell in mice which respond specifically to upward motion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
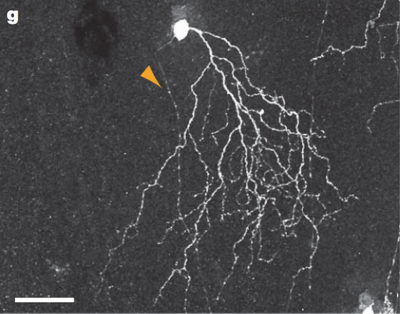
| − | JAM-B cells | + | JAM-B cells are named after Junctional Adhesion Molecule B, the molecular marker first used to define them as a distinct subset of retinal ganglion cells. JAM-B share many traits in addition to the presence of this molecule. They are all OFF RGCs, with asymmetric dendritic arbors aligned in a dorsal-to-ventral direction across the retina (source: Kim et al.) Their deepest importance to the study and categorization of cells in the retina lies in that they were the first RGC to be classified using a molecular marker. |
| + | |||
| + | == Anatomy == | ||
| + | |||
== Physiology == | == Physiology == | ||
| − | + | ||
== Molecules == | == Molecules == | ||
Revision as of 12:16, 24 March 2012
JAM-B cells are a subcategory of retinal ganglion cell in mice which respond specifically to upward motion.
Contents
Introduction
JAM-B cells are named after Junctional Adhesion Molecule B, the molecular marker first used to define them as a distinct subset of retinal ganglion cells. JAM-B share many traits in addition to the presence of this molecule. They are all OFF RGCs, with asymmetric dendritic arbors aligned in a dorsal-to-ventral direction across the retina (source: Kim et al.) Their deepest importance to the study and categorization of cells in the retina lies in that they were the first RGC to be classified using a molecular marker.